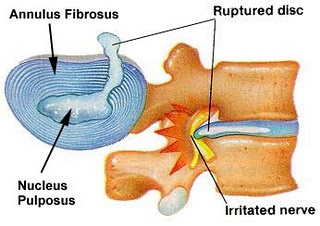
The lumbar disc is comprised of an inner gel and an outer annulus. The lumbar discs provide stability and resiliency to the lumbar spine. Lumbar disc herniation develops because of a tear in the annulus of the lumbar spine; the inner nucleus pulposus extends beyond the tear, comprising a part of the spinal canal.
In many cases, lumbar disc herniation develops insidiously as a result of repeated, small micro tears that develop in conjunction with a degenerative disc. In these cases, patients with lumbar disc herniation may be completely without symptoms. Indeed, imaging studies have revealed that lumbar disc herniation may be present in a sizable number of individuals who have no symptoms.
Many patients with an acute lumbar disc herniations have symptoms of pain or numbness in conjunction with a pinched or compressed nerve. Acute lumbar disc herniation develops because of a sudden and large tear in the annulus, with subsequent rupture of nucleus pulposus material through the tear. Most of these herniations occur posteriorly, that is, toward the back. They also are generally to one side, but occasionally are midline.
If a disc herniation is initially midline, pain is perceived as a deep discomfort in the center of the lower back. Sometimes patients describe a sudden popping sensation. Other times, the patient senses that something is wrong in the lower back, but the pain may not be excruciating. Over days, the tear may enlarge and the disc herniation worsens while symptoms increase.
As a disc herniation enlarges, it generally does so to the right or left of midline. Often, it will compress the lumbar nerve root at that level. Most disc hernations develop between L4-L5, or L5-S1, which are the two lowest segments of the lumbar spine.
These two levels of the lumbar spine are the most mobile and vulnerable segments.
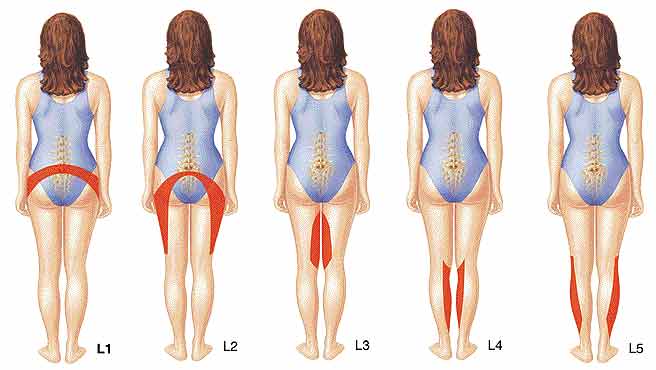
When a nerve root is compressed, there may be associated pain, and pain will normally be perceived in the sensory distribution of that nerve. For example, a herniated disc at L4-5 may compress either the right or left L5 nerve root, which may cause pain radiating down the right or left side of the leg and into the great toe. IF the nerve is severely compressed, there may be numbness (corresponding to the same sensory distribution) or muscle weakness. This demands urgent medical attention.
Patients with acute lumbar disc herniation typically are comfortable lying on their back with knees flexed. Sitting is often uncomfortable, and standing may or may not be comfortable. Patients generally avoid bending forward, and sudden coughing or sneezing can worsen symptoms.
Cause of Lumbar Disc Herniation
The cause of acute lumbar disc herniation is not always apparent. Patients with chronic, degenerative lumbar discs and associated disc herniations often have a genetic predisposition to such degenerative changes. Otherwise, lumbar disc herniations generally occur in the setting of repeated overuse of the lumbar spine or sudden, more severe overuse. In this case, it is not simply the supporting musculature that gives, but the stabilising force of the lumbar spine itself.
Imaging and Diagnostic Studies
Plain X-rays is more for excluding other causes of back and radiating leg pain.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the diagnostic study of choice for lumbar disc herniation. MRI is recommended if the doctor suspects a large disc herniation. MRI should be obtained if the lumbar disc herniation that is not improving with nonsurgical treatment over a few weeks.
Treatment Considerations
- Medicine
- Physiotherapy
- Epidural Injection
- Surgery
Summary Points
- Lumbar disc herniation often develops gradually because of a genetic predisposition to degenerative disc changes.
- Sudden lumbar disc herniation can cause severe pain and sometimes causes leg numbness and weakness.
- Incontinence or severe leg weakness from lumbar disc herniation needs to attend immediately by an orthopaedic surgeon for decompressive spine surgery.
- Most cases of lumbar disc herniation can be managed nonsurgically; over the long term, most patients can return to full activity.
- Patients who develop lumbar disc herniation should try to reflect on significant life stressors that may predispose to spine imbalance.